
Clinical Trunk
Patient care integrated with science.
Clinical Rotations
In the Clinical Trunk, you will enter the clinical environment in your M2 year as a member of a care team, building on your skills from the Scientific Trunk.
The Clinical Trunk comprises two distinct phases:
Building on your Interprofessional Education, Scientific Trunk blocks, Chief Concern course and Doctoring course, you will learn how to function in the clinic. This four-week introductory course gets you ready for Day 1 of the clerkships by focusing on:
- Health care team function
- Clinical problem-solving frameworks
- Integrated science learning with patient cases
- Directed teaching and feedback from Doctoring faculty built around clinical skills
In this phase, you will enter into departmentally organized clinical rotations in seven core clerkships. You will rotate in your teams over the course of 48 weeks, fully prepared with a robust skill set and ready to hit the ground running. The focus is on:
- Immersion into care teams
- Skills of patient care and management
- Professional development
These required core clerkships cover the following departments:
12 weeks each:
- Internal Medicine: Students gain comprehensive experience in diagnosing and managing adult diseases. They work alongside experienced physicians, engaging in diverse activities such as patient rounds, diagnostic assessments, and treatment planning of clinical experiences like chest pain, diabetes, fever and liver disease.
- Surgery and Applied Sciences (a combination of Surgery, Pathology, Anesthesiology, Anatomy and Radiology): Students spend eight weeks immersed in the fast-paced world of surgery, with hands-on experiences in preoperative, operative and postoperative care. Students participate in a variety of procedures, learn essential surgical techniques, and refine their patient management skills. Four weeks focus on advanced anatomy, pathology and radiology, as well as introducing the field of anesthesiology.
Six weeks each:
- OB-GYN: Students develop competence in the primary care of women, practicing their medical history and physical examination skills. They are introduced to a wide range of health issues, including prenatal care, labor and delivery, and gynecologic surgeries.
- Pediatrics: Students obtain the basic skills, knowledge and attitudes to safely and compassionately care for children and their families. They actively engage in the care of patients and will see chronic and acute pediatric illnesses.
Four weeks each:
- Family Medicine: Family Medicine: Students are exposed to ambulatory family medicine in a community-based clinical setting. They have the opportunity to diagnose and manage common problems and chronic diseases, with an emphasis on continuity of care and addressing social determinants of health. Students will enhance skills in communication, history-taking, physical examination and office-based procedures, while experiencing a range of clinical scenarios, including preventive medicine and prenatal care.
- Neurology: Students see a variety of neurologic conditions in inpatient and outpatient settings. In addition, they attend didactic teaching sessions highlighting core concepts in neurology and review basic science topics like neuroanatomy, localization of lesions, neurophysiology and neuropathophysiology.
- Psychiatry: Students learn how to recognize and treat psychiatric illness and gain valuable skills essential to becoming well-rounded physicians. They spend a significant amount of time interviewing patients, allowing them to refine their communication skills and techniques for fostering the patient-physician relationship.
Grading
M2 students receive Honors/High Pass/Pass/Fail grades during core clerkships that are flexible within each grading tier (criterion-based). Students will be graded on their own performance in relation to specified criteria within each clerkship and not graded against their peers (norm-reference). Students will be able to distinguish themselves for their future residency application process while still focusing on learning the material and collaborating with their classmates.
Clinical Trunk Spring Conference
About halfway through the Clinical Trunk, students leave their rotations and come back together over one week to expand their knowledge on the different components within Health System Science and the important roles they play in addressing problems with the current state of our health care in the United States.
USMLE Step 1
The Step 1 exam is taken after the entire Clinical Trunk is complete following a dedicated study period. The Clinical Trunk naturally segues into the Branches phase of the curriculum with the continuity of clinical rotations integrated with scientific learning.
In the Clinical Trunk, you solidify and apply what you learned during your first year through the direct care of patients. Medical students are critically important members of care teams, and you will find many opportunities to bring your unique skills and passion to improve the outcomes for patients.

In addition to the longitudinal elements of the Doctoring Course, Leadership and Paths of Excellence, the Clinical Trunk features:
- Transition to Clerkships course
- Patient evaluations in a variety of clinical settings
- Multidisciplinary clinically driven learning
- Immersion in department-based clinical care teams on core clinical rotations
- Patient Based Scientific Inquiry course
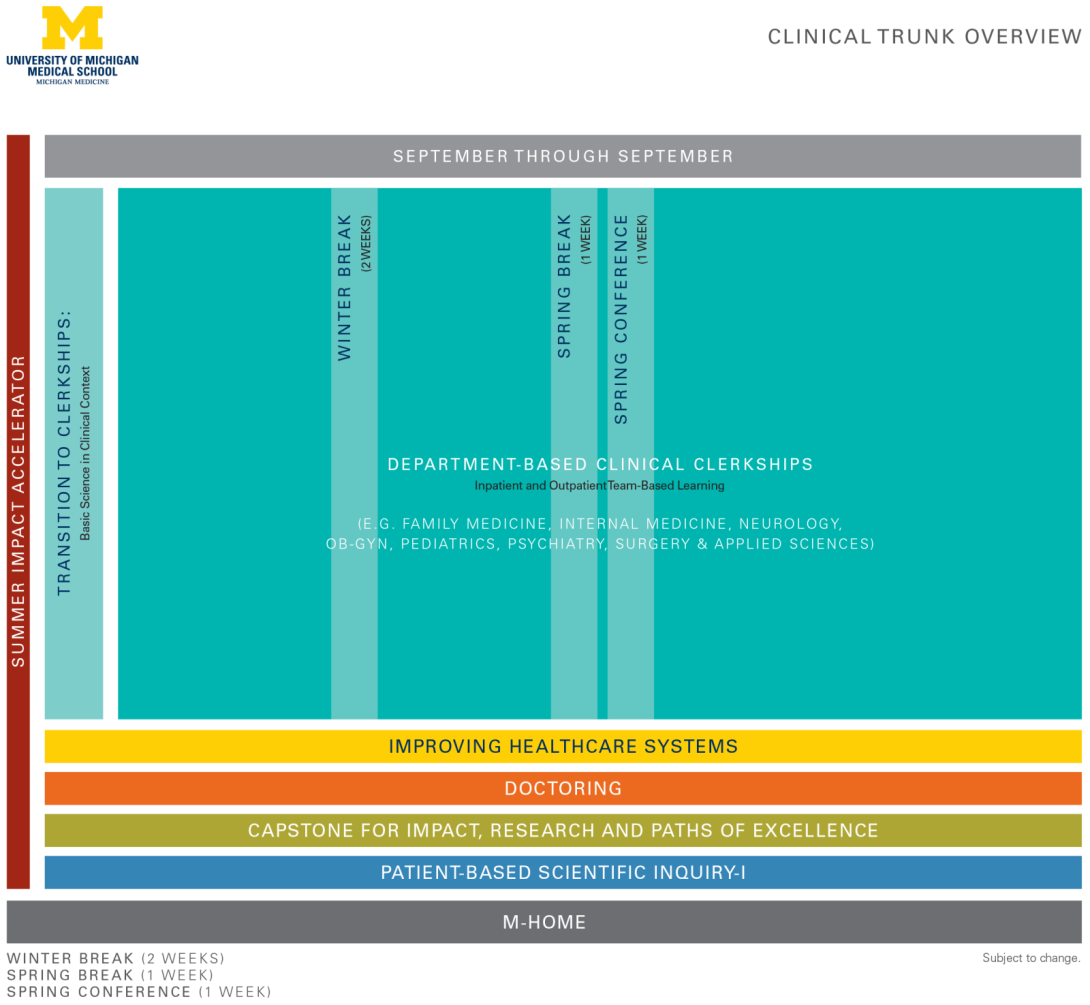
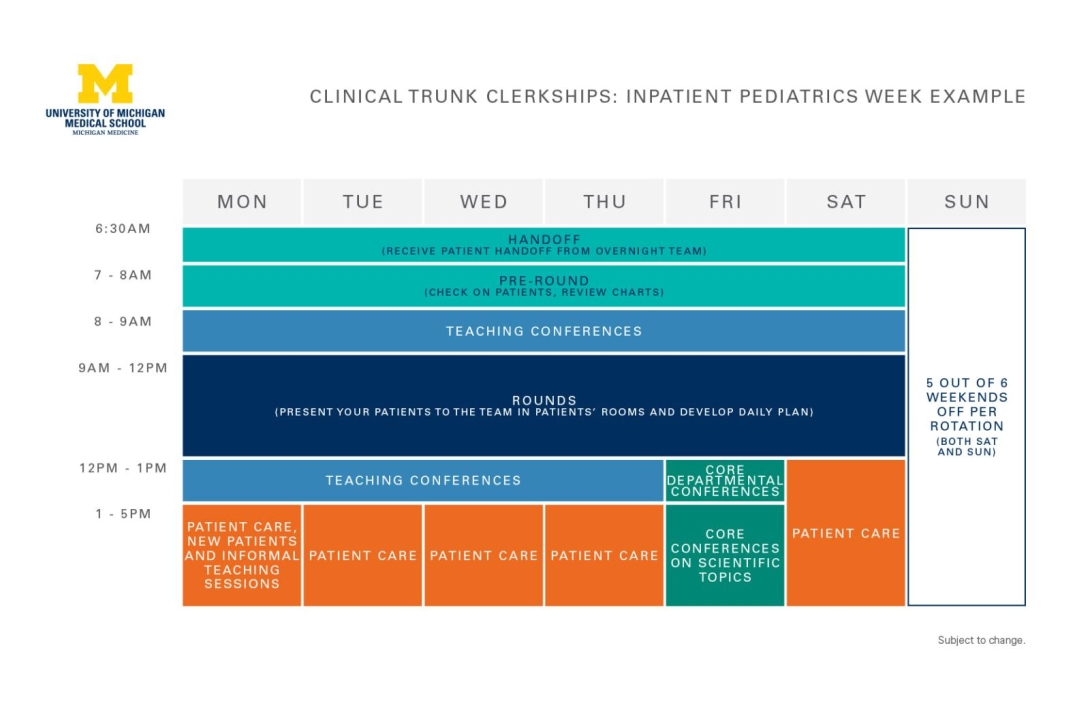
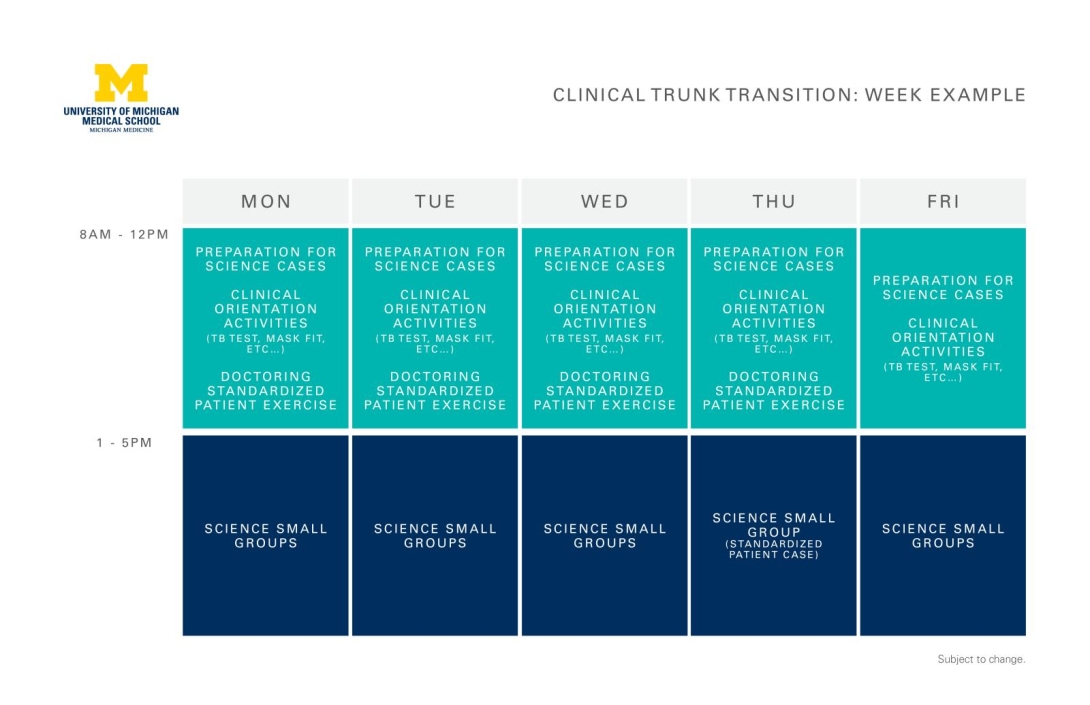
Please note, these diagrams are provided for reference only. Curriculum details are subject to change.